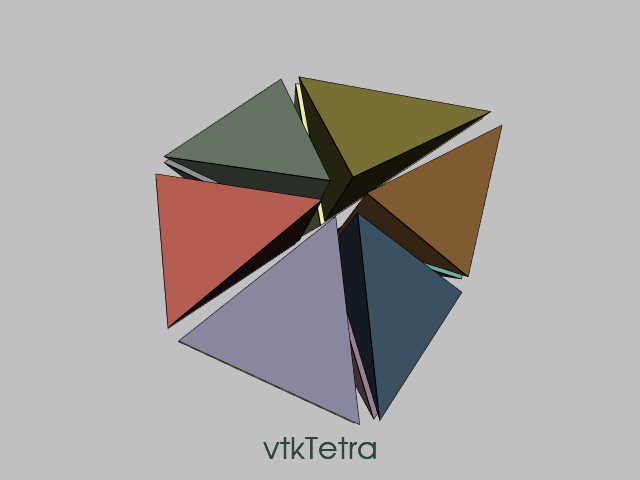
CellTypeSource
Repository source: CellTypeSource
Description¶
This example uses vtkCellTypeSource to generate a vtkUnstructuredGrid. If a cell does not fill a rectangular area or volume, then multiple cells will be generated. For example, a vtkTetra requires 12 cells to fill a cube. A vtkTriangle requires two cells to fill a square. vtkCellTypeSource generates a uniform set of coordinates. The example perturbs those coordinates to illustrate the results of the vtkTessellatorFilter. Also, each cell is passed through vtkShrinkFilter to help identify the cells. Each generated cell also has a unique color.
The example takes an optional argument, a vtkCell name.
For example, to generate vtkTriangles, run
CellTypeSource [vtkTriangle](https://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkTriangle.html)
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
CellTypeSource.py
# !/usr/bin/env python3
from dataclasses import dataclass
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkInteractionStyle
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkRenderingFreeType
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkRenderingOpenGL2
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonColor import (
vtkColorSeries,
vtkNamedColors
)
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonCore import (
vtkIntArray,
vtkLookupTable,
vtkMinimalStandardRandomSequence,
vtkPoints
)
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonDataModel import (
VTK_CUBIC_LINE,
VTK_HEXAHEDRON,
VTK_LINE,
VTK_PYRAMID,
VTK_QUAD,
VTK_QUADRATIC_EDGE,
VTK_QUADRATIC_HEXAHEDRON,
VTK_QUADRATIC_PYRAMID,
VTK_QUADRATIC_QUAD,
VTK_QUADRATIC_TETRA,
VTK_QUADRATIC_TRIANGLE,
VTK_QUADRATIC_WEDGE,
VTK_TETRA,
VTK_TRIANGLE,
VTK_WEDGE,
vtkCellTypes
)
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersGeneral import (
vtkShrinkFilter,
vtkTessellatorFilter
)
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersSources import vtkCellTypeSource
from vtkmodules.vtkInteractionWidgets import (
vtkTextRepresentation,
vtkTextWidget
)
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingCore import (
vtkActor,
vtkDataSetMapper,
vtkRenderWindow,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor,
vtkRenderer,
vtkTextActor,
vtkTextProperty
)
def main():
cell_name = get_program_parameters()
# Store the cell class names in a dictionary.
cell_map = dict()
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_LINE)] = VTK_LINE
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUADRATIC_EDGE)] = VTK_QUADRATIC_EDGE
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_CUBIC_LINE)] = VTK_CUBIC_LINE
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_TRIANGLE)] = VTK_TRIANGLE
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUADRATIC_TRIANGLE)] = VTK_QUADRATIC_TRIANGLE
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUAD)] = VTK_QUAD
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUADRATIC_QUAD)] = VTK_QUADRATIC_QUAD
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_TETRA)] = VTK_TETRA
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_HEXAHEDRON)] = VTK_HEXAHEDRON
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_WEDGE)] = VTK_WEDGE
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_PYRAMID)] = VTK_PYRAMID
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUADRATIC_WEDGE)] = VTK_QUADRATIC_WEDGE
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUADRATIC_PYRAMID)] = VTK_QUADRATIC_PYRAMID
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUADRATIC_HEXAHEDRON)] = VTK_QUADRATIC_HEXAHEDRON
cell_map[vtkCellTypes.GetClassNameFromTypeId(VTK_QUADRATIC_TETRA)] = VTK_QUADRATIC_TETRA
if cell_name not in cell_map:
print('Cell type ', cell_name, ' is not supported.')
return
text_positions = get_text_positions(cell_map.keys(),
justification=TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED,
width=0.5)
source = vtkCellTypeSource(cell_type=cell_map[cell_name])
source.update()
print('Cell: ', cell_name)
original_points = source.output.GetPoints()
points = vtkPoints(number_of_points=source.output.number_of_points)
rng = vtkMinimalStandardRandomSequence()
rng.seed = 5070 # for testing
for i in range(0, points.number_of_points):
perturbation = [0.0] * 3
for j in range(0, 3):
rng.Next()
perturbation[j] = rng.GetRangeValue(-0.1, 0.1)
current_point = [0.0] * 3
original_points.GetPoint(i, current_point)
points.SetPoint(i, current_point[0] + perturbation[0],
current_point[1] + perturbation[1],
current_point[2] + perturbation[2])
source.output.SetPoints(points)
num_cells = source.output.number_of_cells
print('Number of cells: ', num_cells)
id_array = vtkIntArray(number_of_tuples=num_cells)
for i in range(0, num_cells):
id_array.InsertTuple1(i, i + 1)
id_array.name = 'Ids'
source.output.cell_data.AddArray(id_array)
source.output.cell_data.SetActiveScalars('Ids')
shrink = vtkShrinkFilter(shrink_factor=0.8)
tessellate = vtkTessellatorFilter(maximum_number_of_subdivisions=3)
# Create a lookup table to map cell data to colors.
lut = vtkLookupTable()
color_series = vtkColorSeries()
series_enum = color_series.BREWER_QUALITATIVE_SET3
color_series.color_scheme = series_enum
color_series.BuildLookupTable(lut, color_series.ORDINAL)
# Fill in a few known colors, the rest will be generated if needed.
colors = vtkNamedColors()
# Create a renderer, render window, and interactor.
renderer = vtkRenderer(background=colors.GetColor3d('Silver'))
render_window = vtkRenderWindow(size=(640, 480), window_name='CellTypeSource')
render_window.AddRenderer(renderer)
render_window_interactor = vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
render_window_interactor.render_window = render_window
# Create a mapper and actor.
mapper = vtkDataSetMapper(scalar_range=(0, num_cells + 1), lookup_table=lut,
scalar_mode=Mapper.ScalarMode.VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_CELL_DATA,
resolve_coincident_topology=Mapper.ResolveCoincidentTopology.VTK_RESOLVE_POLYGON_OFFSET)
if (source.GetCellType() == VTK_QUADRATIC_PYRAMID or
source.GetCellType() == VTK_QUADRATIC_WEDGE):
source >> shrink >> mapper
else:
source >> shrink >> tessellate >> mapper
actor = vtkActor(mapper=mapper)
actor.property.edge_visibility = True
# actor.property.line_width = 3
text_property = vtkTextProperty(color=colors.GetColor3d('Lamp_Black'), bold=False, italic=False, shadow=False,
font_size=12, justification=TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED)
text_actor = vtkTextActor(input=cell_name,
text_scale_mode=vtkTextActor.TEXT_SCALE_MODE_NONE,
text_property=text_property)
# Create the text representation. Used for positioning the text actor.
text_representation = vtkTextRepresentation(enforce_normalized_viewport_bounds=True)
text_representation.position_coordinate.value = text_positions[cell_name]['p']
text_representation.position2_coordinate.value = text_positions[cell_name]['p2']
# Create the text widget, setting the default renderer and interactor.
text_widget = vtkTextWidget(representation=text_representation, text_actor=text_actor, default_renderer=renderer,
interactor=render_window_interactor, selectable=False)
# Add the actors to the scene.
renderer.AddViewProp(text_actor)
renderer.AddActor(actor)
renderer.ResetCamera()
renderer.active_camera.Azimuth(30)
renderer.active_camera.Elevation(30)
renderer.ResetCameraClippingRange()
# Render and interact.
render_window.Render()
text_widget.On()
render_window_interactor.Start()
def get_text_positions(names, justification=0, vertical_justification=0, width=0.96, height=0.1):
"""
Get viewport positioning information for a list of names.
:param names: The list of names.
:param justification: Horizontal justification of the text, default is left.
:param vertical_justification: Vertical justification of the text, default is bottom.
:param width: Width of the bounding_box of the text in screen coordinates.
:param height: Height of the bounding_box of the text in screen coordinates.
:return: A list of positioning information.
"""
# The gap between the left or right edge of the screen and the text.
dx = 0.02
width = abs(width)
if width > 0.96:
width = 0.96
y0 = 0.01
height = abs(height)
if height > 0.9:
height = 0.9
dy = height
if vertical_justification == TextProperty.VerticalJustification.VTK_TEXT_TOP:
y0 = 1.0 - (dy + y0)
dy = height
if vertical_justification == TextProperty.VerticalJustification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED:
y0 = 0.5 - (dy / 2.0 + y0)
dy = height
name_len_min = 0
name_len_max = 0
first = True
for k in names:
sz = len(k)
if first:
name_len_min = name_len_max = sz
first = False
else:
name_len_min = min(name_len_min, sz)
name_len_max = max(name_len_max, sz)
text_positions = dict()
for k in names:
sz = len(k)
delta_sz = width * sz / name_len_max
if delta_sz > width:
delta_sz = width
if justification == TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED:
x0 = 0.5 - delta_sz / 2.0
elif justification == TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_RIGHT:
x0 = 1.0 - dx - delta_sz
else:
# Default is left justification.
x0 = dx
# For debugging!
# print(
# f'{k:16s}: (x0, y0) = ({x0:3.2f}, {y0:3.2f}), (x1, y1) = ({x0 + delta_sz:3.2f}, {y0 + dy:3.2f})'
# f', width={delta_sz:3.2f}, height={dy:3.2f}')
text_positions[k] = {'p': [x0, y0, 0], 'p2': [delta_sz, dy, 0]}
return text_positions
def get_program_parameters():
import argparse
description = 'Cell Type Source.'
epilogue = '''
You can supply an optional argument consisting of a vtkCell name e.g: vtkTriangle.
The default is vtkTetra.
'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description, epilog=epilogue,
formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument('cell_name', nargs='?', const='vtkTetra', default='vtkTetra', type=str, help='The cell name.')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args.cell_name
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Mapper:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ColorMode:
VTK_COLOR_MODE_DEFAULT: int = 0
VTK_COLOR_MODE_MAP_SCALARS: int = 1
VTK_COLOR_MODE_DIRECT_SCALARS: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ResolveCoincidentTopology:
VTK_RESOLVE_OFF: int = 0
VTK_RESOLVE_POLYGON_OFFSET: int = 1
VTK_RESOLVE_SHIFT_ZBUFFER: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ScalarMode:
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_DEFAULT: int = 0
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_POINT_DATA: int = 1
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_CELL_DATA: int = 2
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_POINT_FIELD_DATA: int = 3
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_CELL_FIELD_DATA: int = 4
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_FIELD_DATA: int = 5
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class TextProperty:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Justification:
VTK_TEXT_LEFT: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_RIGHT: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class VerticalJustification:
VTK_TEXT_BOTTOM: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_TOP: int = 2
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()