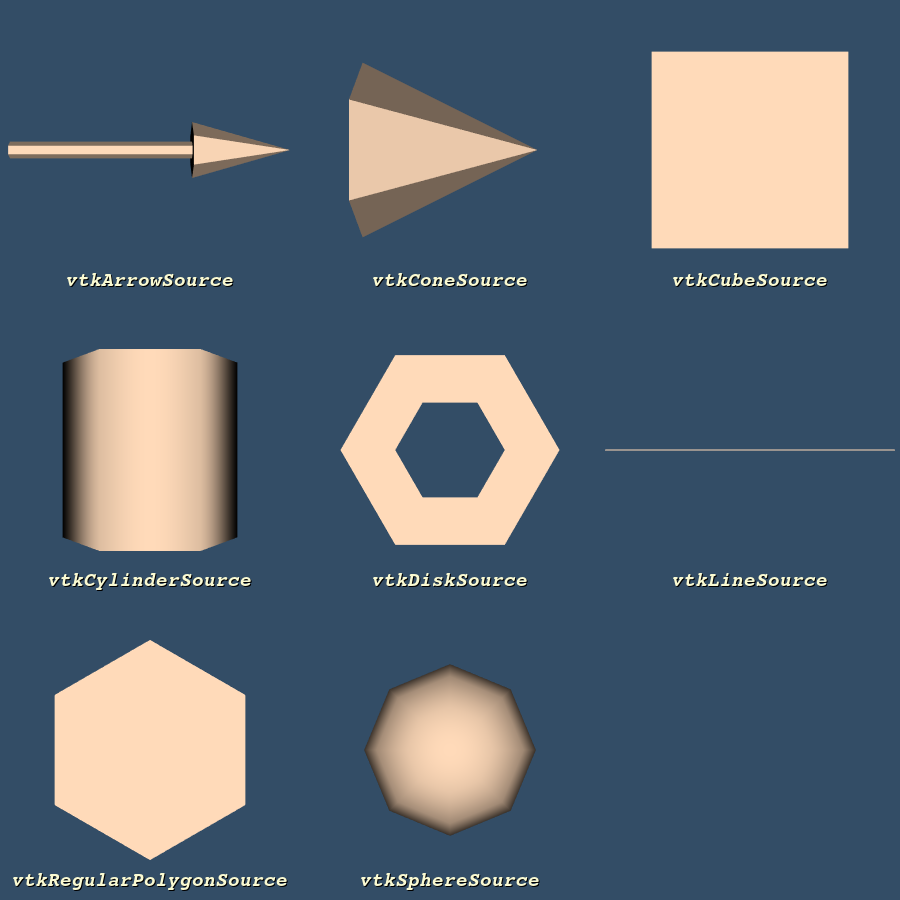
GeometricObjectsDemo
Repository source: GeometricObjectsDemo
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
GeometricObjectsDemo.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from dataclasses import dataclass
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkInteractionStyle
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkRenderingFreeType
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkRenderingOpenGL2
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonColor import vtkNamedColors
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersSources import (
vtkArrowSource,
vtkConeSource,
vtkCubeSource,
vtkCylinderSource,
vtkDiskSource,
vtkLineSource,
vtkRegularPolygonSource,
vtkSphereSource
)
from vtkmodules.vtkInteractionStyle import vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera
from vtkmodules.vtkInteractionWidgets import (
vtkTextRepresentation,
vtkTextWidget
)
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingCore import (
vtkActor,
vtkPolyDataMapper,
vtkRenderWindow,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor,
vtkRenderer,
vtkTextActor,
vtkTextProperty
)
def main():
colors = vtkNamedColors()
# Set the background color.
colors.SetColor("BkgColor", 51, 77, 102, 255)
# Create container to hold the 3D object generators (sources)
geometric_object_sources = list()
# Populate the container with the various object sources to be demonstrated
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkArrowSource())
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkConeSource())
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkCubeSource())
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkCylinderSource())
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkDiskSource())
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkLineSource())
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkRegularPolygonSource())
geometric_object_sources.append(vtkSphereSource())
# Define the size of the grid that will hold the objects.
grid_cols = 3
grid_rows = 3
# Define side length (in pixels) of each renderer square.
renderer_size = 300
size = (renderer_size * grid_cols, renderer_size * grid_rows)
render_window = vtkRenderWindow(size=size, window_name='GeometricObjectsDemo')
interactor = vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
interactor.render_window = render_window
style = vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera()
interactor.interactor_stype = style
# Create one text property for all.
text_property = vtkTextProperty(color=colors.GetColor3d('LightGoldenrodYellow'), bold=True, italic=True,
shadow=True, font_family_as_string='Courier',
font_size=16, justification=TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED)
# Position text according to its length and centered in the viewport.
surface_names = list()
for i in range(0, len(geometric_object_sources)):
surface_names.append(geometric_object_sources[i].class_name)
text_positions = get_text_positions(surface_names, justification=TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED)
# back_property = vtkProperty(color=colors.GetColor3d('Tomato'))
mappers = list()
actors = list()
text_representations = list()
text_actors = list()
text_widgets = list()
for row in range(0, grid_rows):
for col in range(0, grid_cols):
index = row * grid_cols + col
# Set the renderer's viewport dimensions (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax) within the render window.
# Note that for the Y values, we need to subtract the row index from grid_rows
# because the viewport Y axis points upwards, but we want to draw the grid from top to down.
viewport = (
float(col) / grid_cols,
float(grid_rows - row - 1) / grid_rows,
float(col + 1) / grid_cols,
float(grid_rows - row) / grid_rows
)
# Create a renderer for this grid cell.
renderer = vtkRenderer(background=colors.GetColor3d('BkgColor'), viewport=viewport)
# Add the corresponding actor and label for this grid cell, if they exist.
if index < len(geometric_object_sources):
name = geometric_object_sources[index].class_name
# Create the mappers and actors for each object.
mappers.append(vtkPolyDataMapper())
geometric_object_sources[index] >> mappers[index]
actors.append(vtkActor(mapper=mappers[index]))
actors[index].property.color = colors.GetColor3d('PeachPuff')
# actors[index].backface_property = back_property
renderer.AddActor(actors[index])
# Create the text actor and representation.
text_actors.append(
vtkTextActor(input=geometric_object_sources[index].class_name,
text_scale_mode=vtkTextActor.TEXT_SCALE_MODE_NONE,
text_property=text_property))
# Create the text representation. Used for positioning the text actor.
text_representations.append(vtkTextRepresentation(enforce_normalized_viewport_bounds=True))
text_representations[index].position_coordinate.value = text_positions[name]['p']
text_representations[index].position2_coordinate.value = text_positions[name]['p2']
# Create the text widget, setting the default renderer and interactor.
text_widgets.append(
vtkTextWidget(representation=text_representations[index], text_actor=text_actors[index],
default_renderer=renderer, interactor=interactor, selectable=False))
renderer.ResetCamera()
render_window.AddRenderer(renderer)
render_window.Render()
for i in range(0, len(geometric_object_sources)):
text_widgets[i].On()
interactor.Start()
def get_text_positions(names, justification=0, vertical_justification=0, width=0.96, height=0.1):
"""
Get viewport positioning information for a list of names.
:param names: The list of names.
:param justification: Horizontal justification of the text, default is left.
:param vertical_justification: Vertical justification of the text, default is bottom.
:param width: Width of the bounding_box of the text in screen coordinates.
:param height: Height of the bounding_box of the text in screen coordinates.
:return: A list of positioning information.
"""
# The gap between the left or right edge of the screen and the text.
dx = 0.02
width = abs(width)
if width > 0.96:
width = 0.96
y0 = 0.01
height = abs(height)
if height > 0.9:
height = 0.9
dy = height
if vertical_justification == TextProperty.VerticalJustification.VTK_TEXT_TOP:
y0 = 1.0 - (dy + y0)
dy = height
if vertical_justification == TextProperty.VerticalJustification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED:
y0 = 0.5 - (dy / 2.0 + y0)
dy = height
name_len_min = 0
name_len_max = 0
first = True
for k in names:
sz = len(k)
if first:
name_len_min = name_len_max = sz
first = False
else:
name_len_min = min(name_len_min, sz)
name_len_max = max(name_len_max, sz)
text_positions = dict()
for k in names:
sz = len(k)
delta_sz = width * sz / name_len_max
if delta_sz > width:
delta_sz = width
if justification == TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED:
x0 = 0.5 - delta_sz / 2.0
elif justification == TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_RIGHT:
x0 = 1.0 - dx - delta_sz
else:
# Default is left justification.
x0 = dx
# For debugging!
# print(
# f'{k:16s}: (x0, y0) = ({x0:3.2f}, {y0:3.2f}), (x1, y1) = ({x0 + delta_sz:3.2f}, {y0 + dy:3.2f})'
# f', width={delta_sz:3.2f}, height={dy:3.2f}')
text_positions[k] = {'p': [x0, y0, 0], 'p2': [delta_sz, dy, 0]}
return text_positions
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class TextProperty:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Justification:
VTK_TEXT_LEFT: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_RIGHT: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class VerticalJustification:
VTK_TEXT_BOTTOM: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_TOP: int = 2
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()