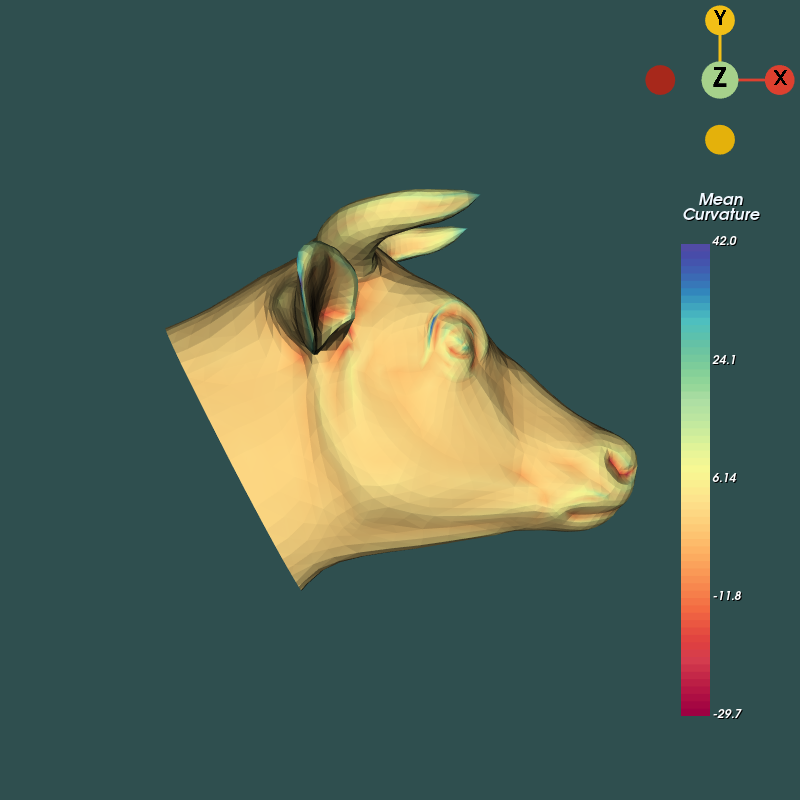
Curvatures
Repository source: Curvatures
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
Curvatures.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import copy
from dataclasses import dataclass
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from vtk.util import numpy_support
from vtkmodules.numpy_interface import dataset_adapter as dsa
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonColor import (
vtkColorSeries,
vtkNamedColors
)
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonCore import (
VTK_DOUBLE,
vtkIdList
)
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersCore import (
vtkFeatureEdges,
vtkGenerateIds
)
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersGeneral import vtkCurvatures
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
from vtkmodules.vtkIOXML import (
vtkXMLPolyDataReader,
vtkXMLPolyDataWriter,
vtkXMLWriterBase,
)
from vtkmodules.vtkInteractionWidgets import (
vtkCameraOrientationWidget,
vtkScalarBarRepresentation,
vtkScalarBarWidget,
)
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingAnnotation import vtkScalarBarActor
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingCore import (
vtkActor,
vtkColorTransferFunction,
vtkPolyDataMapper,
vtkRenderWindow,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor,
vtkRenderer,
vtkTextProperty
)
def get_program_parameters(argv):
import argparse
import textwrap
description = 'Calculate Gauss or Mean Curvature.'
epilogue = textwrap.dedent('''
''')
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter, description=description,
epilog=epilogue)
parser.add_argument('file_name', help=' e.g. cowHead.vtp.')
parser.add_argument('-i', default=16, type=int, help='The color map index e.g. 16.')
parser.add_argument('-g', help='Use Gaussian Curvature.', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('-w', help='Write out the polydata.', action='store_true')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args.file_name, args.i, args.g, args.w
def main(argv):
file_name, color_map_idx, gaussian_curvature, save_pd = get_program_parameters(argv)
if not Path(file_name).is_file():
print(f'The path: {file_name} does not exist.')
return
if gaussian_curvature:
curvature = 'Gauss_Curvature'
else:
curvature = 'Mean_Curvature'
reader = vtkXMLPolyDataReader(file_name=file_name)
source = reader.update().output
if gaussian_curvature:
cc = vtkCurvatures(curvature_type=Curvatures.CurvatureType.VTK_CURVATURE_GAUSS)
else:
cc = vtkCurvatures(curvature_type=Curvatures.CurvatureType.VTK_CURVATURE_MEAN)
p = (source >> cc).update().output
adjust_edge_curvatures(p, curvature)
source.point_data.AddArray(p.point_data.GetAbstractArray(curvature))
scalar_range = source.point_data.GetScalars(curvature).range
if save_pd:
writer = vtkXMLPolyDataWriter(input_data=source, file_name='Source.vtp', data_mode=vtkXMLWriterBase.Ascii)
writer.Write()
# Build a lookup table
color_series = vtkColorSeries(color_scheme=color_map_idx)
print(f'Using color scheme #: {color_series.GetColorScheme()}, {color_series.GetColorSchemeName()}')
lut = vtkColorTransferFunction(color_space=ColorTransferFunction.ColorSpace.VTK_CTF_HSV)
# Use a color series to create a transfer function
for i in range(0, color_series.GetNumberOfColors()):
color = color_series.GetColor(i)
double_color = list(map(lambda x: x / 255.0, color))
t = scalar_range[0] + (scalar_range[1] - scalar_range[0]) / (color_series.GetNumberOfColors() - 1) * i
lut.AddRGBPoint(t, double_color[0], double_color[1], double_color[2])
colors = vtkNamedColors()
# Create a mapper and actor.
mapper = vtkPolyDataMapper(scalar_range=scalar_range, lookup_table=lut,
scalar_mode=Mapper.ScalarMode.VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_POINT_FIELD_DATA)
mapper.SelectColorArray(curvature)
actor = vtkActor(mapper=mapper)
p >> mapper
window_width = 800
window_height = 800
# Create a renderer, render window, and interactor
renderer = vtkRenderer(background=colors.GetColor3d('DarkSlateGray'))
ren_win = vtkRenderWindow(size=(window_width, window_height), window_name='Curvatures')
ren_win.AddRenderer(renderer)
iren = vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
iren.render_window = ren_win
# Important: The interactor must be set prior to enabling the widget.
iren.render_window = ren_win
text_property = vtkTextProperty(color=colors.GetColor3d('AliceBlue'), bold=True, italic=True, shadow=True,
font_size=16,
justification=TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_LEFT)
# Set up the scalar bar properties.
scalar_bar_properties = ScalarBarProperties()
if gaussian_curvature:
scalar_bar_properties.title_text = 'Gaussian\nCurvature\n'
else:
scalar_bar_properties.title_text = 'Mean\nCurvature\n'
scalar_bar_properties.position_v = {'p': (0.85, 0.1), 'p2': (0.125, 0.375)}
scalar_bar_properties.lut = lut
scalar_bar_widget = make_scalar_bar_widget(scalar_bar_properties, text_property, text_property, renderer, iren)
cam_orient_manipulator = vtkCameraOrientationWidget(parent_renderer=renderer)
# Enable the widget.
cam_orient_manipulator.On()
# Add the actors to the scene
renderer.AddActor(actor)
renderer.SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d('DarkSlateGray'))
# Render and interact
ren_win.Render()
iren.Start()
def adjust_edge_curvatures(source, curvature_name, epsilon=1.0e-08):
"""
This function adjusts curvatures along the edges of the surface by replacing
the value with the average value of the curvatures of points in the neighborhood.
:param source: The vtkCurvatures object.
:param curvature_name: The name of the curvature, 'Gauss_Curvature' or 'Mean_Curvature'.
:param epsilon: Absolute curvature values less than this will be set to zero.
:return:
"""
def point_neighbourhood(pt_id):
"""
Extract the topological neighbors for point.
:param pt_id: The point id.
:return: The neighbour ids.
"""
cell_ids = vtkIdList()
source.GetPointCells(pt_id, cell_ids)
neighbour = set()
for cell_idx in range(0, cell_ids.GetNumberOfIds()):
cell_id = cell_ids.GetId(cell_idx)
cell_point_ids = vtkIdList()
source.GetCellPoints(cell_id, cell_point_ids)
for cell_pt_idx in range(0, cell_point_ids.GetNumberOfIds()):
neighbour.add(cell_point_ids.GetId(cell_pt_idx))
return neighbour
def compute_distance(pt_id_a, pt_id_b):
"""
Compute the distance between two points given their ids.
:param pt_id_a: First point.
:param pt_id_b: Second point.
:return: The distance.
"""
pt_a = np.array(source.GetPoint(pt_id_a))
pt_b = np.array(source.GetPoint(pt_id_b))
return np.linalg.norm(pt_a - pt_b)
# Get the active scalars
source.point_data.SetActiveScalars(curvature_name)
np_source = dsa.WrapDataObject(source)
curvatures = np_source.PointData[curvature_name]
# Get the boundary point IDs.
array_name = 'ids'
id_filter = vtkGenerateIds(point_ids=True, cell_ids=False,
point_ids_array_name=array_name,
cell_ids_array_name=array_name)
edges = vtkFeatureEdges(boundary_edges=True, manifold_edges=False,
non_manifold_edges=False, feature_edges=False)
(source >> id_filter >> edges).update()
edge_array = edges.output.GetPointData().GetArray(array_name)
boundary_ids = []
for i in range(edges.output.GetNumberOfPoints()):
boundary_ids.append(edge_array.GetValue(i))
# Remove duplicate Ids.
p_ids_set = set(boundary_ids)
# Iterate over the edge points and compute the curvature as the weighted
# average of the neighbours.
count_invalid = 0
for p_id in boundary_ids:
p_ids_neighbors = point_neighbourhood(p_id)
# Keep only interior points.
p_ids_neighbors -= p_ids_set
# Compute distances and extract curvature values.
curvs = [curvatures[p_id_n] for p_id_n in p_ids_neighbors]
dists = [compute_distance(p_id_n, p_id) for p_id_n in p_ids_neighbors]
curvs = np.array(curvs)
dists = np.array(dists)
curvs = curvs[dists > 0]
dists = dists[dists > 0]
if len(curvs) > 0:
weights = 1 / np.array(dists)
weights /= weights.sum()
new_curv = np.dot(curvs, weights)
else:
# Corner case.
count_invalid += 1
# Assuming the curvature of the point is planar.
new_curv = 0.0
# Set the new curvature value.
curvatures[p_id] = new_curv
# Set small values to zero.
if epsilon != 0.0:
curvatures = np.where(abs(curvatures) < epsilon, 0, curvatures)
curv = numpy_support.numpy_to_vtk(num_array=curvatures.ravel(),
deep=True,
array_type=VTK_DOUBLE)
curv.name = curvature_name
source.point_data.RemoveArray(curvature_name)
source.point_data.AddArray(curv)
source.point_data.active_scalars = curvature_name
class ScalarBarProperties:
"""
The properties needed for scalar bars.
"""
named_colors = vtkNamedColors()
lut = None
# These are in pixels
maximum_dimensions = {'width': 100, 'height': 260}
title_text = '',
number_of_labels: int = 5
label_format = '{:0.2f}'
# Orientation vertical=True, horizontal=False.
orientation: bool = True
# Horizontal and vertical positioning.
# These are the default positions, don't change these.
default_v = {'p': (0.85, 0.1), 'p2': (0.1, 0.7)}
default_h = {'p': (0.1, 0.1), 'p2': (0.7, 0.1)}
# Modify these as needed.
position_v = copy.deepcopy(default_v)
position_h = copy.deepcopy(default_h)
def make_scalar_bar_widget(scalar_bar_properties, title_text_property, label_text_property, renderer,
interactor):
"""
Make a scalar bar widget.
:param scalar_bar_properties: The lookup table, title name, maximum dimensions in pixels and position.
:param title_text_property: The properties for the title.
:param label_text_property: The properties for the labels.
:param renderer: The default renderer.
:param interactor: The vtkInteractor.
:return: The scalar bar widget.
"""
sb_actor = vtkScalarBarActor(lookup_table=scalar_bar_properties.lut, title=scalar_bar_properties.title_text,
unconstrained_font_size=True,
number_of_labels=scalar_bar_properties.number_of_labels,
title_text_property=title_text_property, label_text_property=label_text_property,
label_format=scalar_bar_properties.label_format,
)
sb_rep = vtkScalarBarRepresentation(enforce_normalized_viewport_bounds=True,
orientation=scalar_bar_properties.orientation)
# Set the position.
sb_rep.position_coordinate.SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport()
sb_rep.position2_coordinate.SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport()
if scalar_bar_properties.orientation:
sb_rep.position_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_v['p']
sb_rep.position2_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_v['p2']
else:
sb_rep.position_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_h['p']
sb_rep.position2_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_h['p2']
widget = vtkScalarBarWidget(representation=sb_rep, scalar_bar_actor=sb_actor, default_renderer=renderer,
interactor=interactor, enabled=True)
return widget
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ColorTransferFunction:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ColorSpace:
VTK_CTF_RGB: int = 0
VTK_CTF_HSV: int = 1
VTK_CTF_LAB: int = 2
VTK_CTF_DIVERGING: int = 3
VTK_CTF_LAB_CIEDE2000: int = 4
VTK_CTF_STEP: int = 5
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Scale:
VTK_CTF_LINEAR: int = 0
VTK_CTF_LOG10: int = 1
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Curvatures:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class CurvatureType:
VTK_CURVATURE_GAUSS: int = 0
VTK_CURVATURE_MEAN: int = 1
VTK_CURVATURE_MAXIMUM: int = 2
VTK_CURVATURE_MINIMUM: int = 3
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Mapper:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ColorMode:
VTK_COLOR_MODE_DEFAULT: int = 0
VTK_COLOR_MODE_MAP_SCALARS: int = 1
VTK_COLOR_MODE_DIRECT_SCALARS: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ResolveCoincidentTopology:
VTK_RESOLVE_OFF: int = 0
VTK_RESOLVE_POLYGON_OFFSET: int = 1
VTK_RESOLVE_SHIFT_ZBUFFER: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ScalarMode:
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_DEFAULT: int = 0
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_POINT_DATA: int = 1
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_CELL_DATA: int = 2
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_POINT_FIELD_DATA: int = 3
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_CELL_FIELD_DATA: int = 4
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_FIELD_DATA: int = 5
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class TextProperty:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Justification:
VTK_TEXT_LEFT: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_RIGHT: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class VerticalJustification:
VTK_TEXT_BOTTOM: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_TOP: int = 2
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
main(sys.argv)