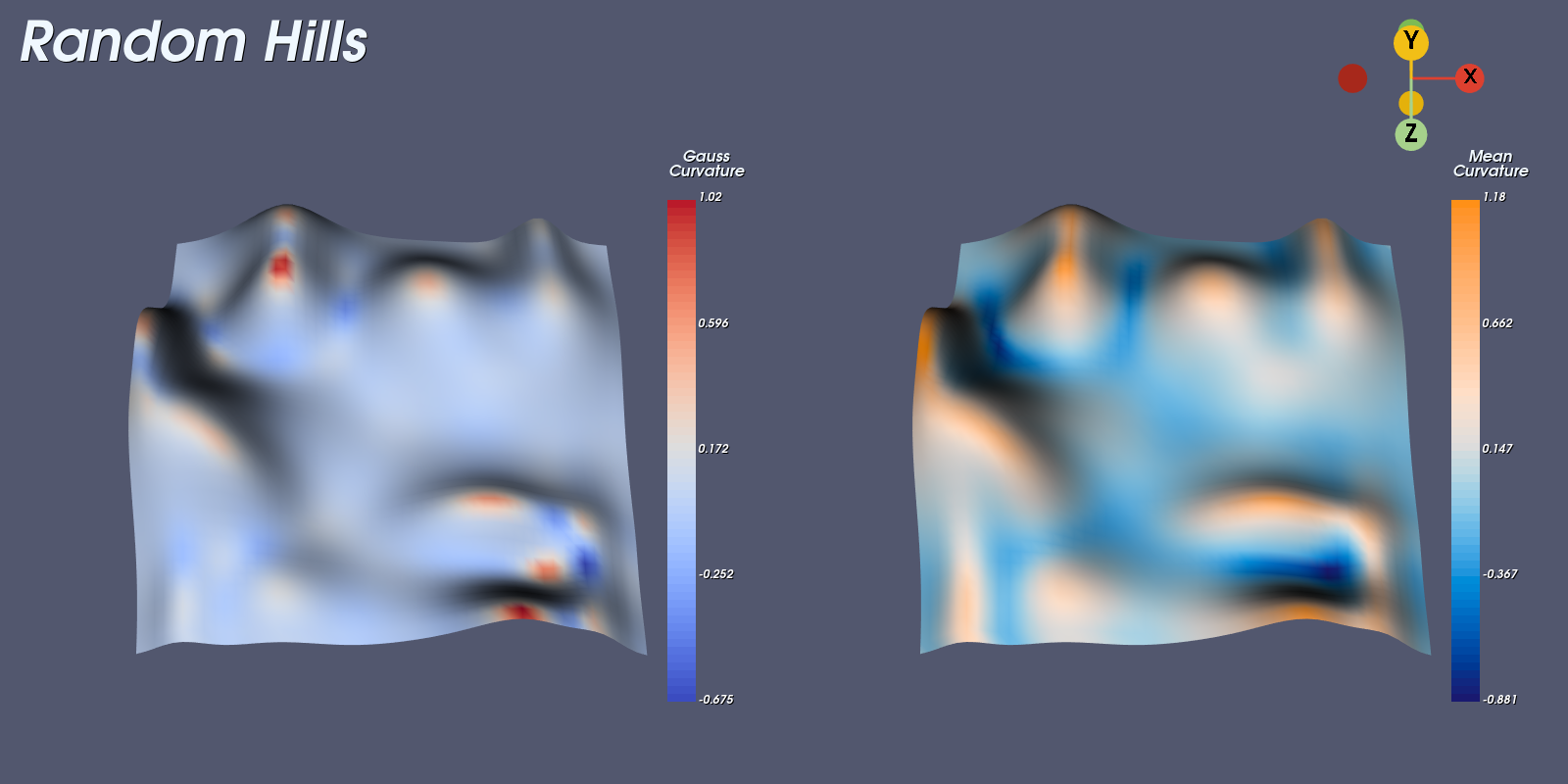
CurvaturesAdjustEdges
Repository source: CurvaturesAdjustEdges
Description¶
This example demonstrates how to calculate Gaussian and Mean curvatures for a vtkPolyData source. Since edges can produce large discrepancies to curvatures, edge adjustment can be applied. If we know the geometry of the surface we can also modify the curvatures.
Functions are provided to achieve these aims.
A histogram of the frequencies is also output to the console. This is useful if you want to get an idea of the distribution of the scalars in each band.
This example was inspired by these discussions:
- vtkCurvatures yields unreasonably large values along borders
- How to extract the ids of the boundary points of a surface?
Thanks to everyone involved in these discussions.
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
CurvaturesAdjustEdges.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import copy
import math
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
from dataclasses import dataclass
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from vtk.util import numpy_support
from vtkmodules.numpy_interface import dataset_adapter as dsa
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonColor import vtkNamedColors
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonComputationalGeometry import (
vtkParametricBour,
vtkParametricEnneper,
vtkParametricMobius,
vtkParametricRandomHills,
vtkParametricTorus
)
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonCore import (
VTK_DOUBLE,
vtkFloatArray,
vtkIdList,
vtkLookupTable,
vtkPoints
)
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonDataModel import (
vtkCellArray,
vtkTriangle
)
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonDataModel import vtkPolyData
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonTransforms import vtkTransform
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersCore import (
vtkElevationFilter,
vtkFeatureEdges,
vtkGenerateIds,
vtkPolyDataNormals,
vtkPolyDataTangents,
vtkTriangleFilter
)
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersGeneral import (
vtkCurvatures,
vtkTransformPolyDataFilter
)
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersModeling import vtkLinearSubdivisionFilter
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersSources import (
vtkCubeSource,
vtkParametricFunctionSource,
vtkTexturedSphereSource
)
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
from vtkmodules.vtkIOXML import vtkXMLPolyDataWriter
from vtkmodules.vtkInteractionStyle import vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera
from vtkmodules.vtkInteractionWidgets import (
vtkCameraOrientationWidget,
vtkOrientationMarkerWidget,
vtkScalarBarRepresentation,
vtkScalarBarWidget,
vtkTextRepresentation,
vtkTextWidget
)
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingAnnotation import vtkAxesActor, vtkScalarBarActor
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingCore import (
vtkActor,
vtkColorTransferFunction,
vtkPolyDataMapper,
vtkRenderWindow,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor,
vtkRenderer,
vtkTextActor,
vtkTextProperty
)
def get_program_parameters():
import argparse
description = 'Demonstrates Gaussian and Mean curvatures on a surface.'
epilogue = '''
For example: -s"Random Hills" -f
Will display the curvatures along with normals on the surface colored by elevation.
'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description, epilog=epilogue,
formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument('surface_name', nargs='?', default='random hills',
help='The name of the surface - enclose the name in quotes if it has spaces.')
parser.add_argument('-f', '--frequency_table', action='store_true', help='Display the frequency table.')
parser.add_argument('-omw', action='store_false',
help='Use an OrientationMarkerWidget instead of a CameraOrientationWidget.')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args.surface_name, args.frequency_table, args.omw
def main(argv):
surface_name, frequency_table, use_camera_omw = get_program_parameters()
available_surfaces = ['bour', 'cube', 'enneper', 'hills', 'mobius', 'random hills', 'sphere', 'torus']
# Surfaces whose curvatures need to be adjusted along the edges of the surface or constrained.
needs_adjusting = ['bour', 'enneper', 'hills', 'random hills', 'torus']
surface_name = ' '.join(surface_name.lower().replace('_', ' ').split())
if surface_name not in available_surfaces:
print('Nonexistent surface:', surface_name)
print('Available surfaces are:')
asl = sorted(available_surfaces)
asl = [asl[i].title() for i in range(0, len(asl))]
asl = [asl[i:i + 5] for i in range(0, len(asl), 5)]
for i in range(0, len(asl)):
s = ', '.join(asl[i])
if i < len(asl) - 1:
s += ','
print(f' {s}')
print('If a name has spaces in it, delineate the name with quotes e.g. "random hills"')
return
Surface = namedtuple('Surface', 'name source')
surface = Surface(surface_name, get_source(surface_name, available_surfaces))
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Get the filters, scalar range of curvatures and the lookup tables.
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Use an ordered dictionary as we want the keys in a specific order.
curvatures = OrderedDict()
curvatures['Gauss_Curvature'] = generate_gaussian_curvatures(surface, needs_adjusting,
frequency_table=frequency_table)
curvatures['Mean_Curvature'] = generate_mean_curvatures(surface, needs_adjusting, frequency_table=frequency_table)
# Let's visualise what we have done.
colors = vtkNamedColors()
colors.SetColor('ParaViewBlueGrayBkg', 84, 89, 109, 255)
colors.SetColor('ParaViewWarmGrayBkg', 98, 93, 90, 255)
window_height = 512
window_width = 2 * window_height
ren_win = vtkRenderWindow(size=(window_width, window_height), window_name=f'{Path(argv[0]).name:s}')
iren = vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
iren.render_window = ren_win
style = vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera()
iren.interactor_style = style
# Define viewport ranges [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
viewports = dict()
viewports['Gauss_Curvature'] = [0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0]
viewports['Mean_Curvature'] = [0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0]
# Build the renderers and add them to the render window.
renderers = list()
scalar_bar_widgets = dict()
# Position the source name according to its length.
text_positions = get_text_positions(available_surfaces,
justification=TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_LEFT,
vertical_justification=TextProperty.VerticalJustification.VTK_TEXT_TOP,
width=0.45)
text_property = vtkTextProperty(color=colors.GetColor3d('AliceBlue'), bold=True, italic=True, shadow=True,
font_size=16,
justification=TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_LEFT)
text_actor = vtkTextActor(input=surface_name.title(), text_scale_mode=vtkTextActor.TEXT_SCALE_MODE_NONE,
text_property=text_property)
# Create the text representation. Used for positioning the text actor.
text_representation = vtkTextRepresentation(enforce_normalized_viewport_bounds=True)
text_representation.position_coordinate.value = text_positions[surface.name]['p']
text_representation.position2_coordinate.value = text_positions[surface.name]['p2']
text_widget = vtkTextWidget(representation=text_representation, text_actor=text_actor, interactor=iren,
selectable=False)
# These surfaces have just one curvature value.
single_gauss_curv = ['bour', 'enneper', 'cube', 'mobius', 'sphere']
single_mean_curv = ['bour', 'enneper', 'cube', 'sphere']
first = True
for k, v in curvatures.items():
src_mapper = vtkPolyDataMapper(scalar_range=v['scalar_range_curvatures'],
lookup_table=v['lut'],
scalar_mode=Mapper.ScalarMode.VTK_SCALAR_MODE_DEFAULT)
src_actor = vtkActor(mapper=src_mapper)
v['surface'] >> src_mapper
renderer = vtkRenderer(background=colors.GetColor3d('ParaViewWarmGrayBkg'))
if first:
text_widget.default_renderer = renderer
first = False
renderer.viewport = viewports[k]
renderer.AddActor(src_actor)
scalar_bar_properties = ScalarBarProperties()
scalar_bar_properties.title_text = k.replace('_', ' ') + '\n'
scalar_bar_properties.number_of_labels = min(5, curvatures[k]['scalar_bar_labels'])
scalar_bar_properties.lut = curvatures[k]['lut']
scalar_bar_properties.orientation = False
if k == 'Gauss_Curvature':
if surface_name in single_gauss_curv:
scalar_bar_properties.position_h = {'p': (0.3, 0.05), 'p2': (0.35, 0.1)}
if k == 'Mean_Curvature':
if surface_name in single_mean_curv:
scalar_bar_properties.position_h = {'p': (0.3, 0.05), 'p2': (0.35, 0.1)}
scalar_bar_widgets[k] = make_scalar_bar_widget(scalar_bar_properties, text_property, text_property, renderer,
iren)
renderers.append(renderer)
for renderer in renderers:
ren_win.AddRenderer(renderer)
# Enable the widgets.
if use_camera_omw:
cam_orient_manipulator = vtkCameraOrientationWidget(parent_renderer=renderers[0])
# Enable the widget.
cam_orient_manipulator.On()
else:
rgb = [0.0] * 4
colors.GetColor("Carrot", rgb)
rgb = tuple(rgb[:3])
widget = vtkOrientationMarkerWidget(orientation_marker=vtkAxesActor(),
interactor=iren, default_renderer=renderers[1],
outline_color=rgb, viewport=(0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0), zoom=1.5, enabled=True,
interactive=True)
for k in curvatures.keys():
scalar_bar_widgets[k].On()
text_widget.On()
camera = None
for i in range(0, len(renderers)):
if i == 0:
camera = renderers[0].active_camera
camera.Elevation(60)
# This moves the window center slightly to ensure that
# the whole surface is not obscured by the scalar bars.
camera.window_center = (0.0, -0.15)
else:
renderers[i].active_camera = camera
renderers[i].ResetCamera()
renderers[0].active_camera.Zoom(0.95)
ren_win.Render()
iren.Start()
def generate_gaussian_curvatures(surface, needs_adjusting, frequency_table=False):
"""
Generate the Gaussian curvatures on the surface.
:param surface: The surface.
:param needs_adjusting: Surfaces whose curvatures need to be adjusted along the edges of the surface or constrained.
:param frequency_table: True if a frequency table is to be displayed.
:return: Return the surface, the scalar ranges of the curvatures along with the lookup tables.
"""
name = surface.name
source = surface.source
curvature = 'Gauss_Curvature'
scalar_bar_labels = 5
curvatures = vtkCurvatures(curvature_type=Curvatures.CurvatureType.VTK_CURVATURE_GAUSS)
p = (source >> curvatures).update().output
if name in needs_adjusting:
adjust_edge_curvatures(p, curvature)
if name == 'bour':
# Gaussian curvature is -1/(r(r+1)^4)
r = 1
gauss_curvature = -1 / (r * (r + 1) ** 4)
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, gauss_curvature, gauss_curvature)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
if name == 'enneper':
# Gaussian curvature is -4/(1 + r^2)^4
r = 1
gauss_curvature = -4 / ((1 + r ** 2) ** 4)
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, gauss_curvature, gauss_curvature)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
if name == 'cube':
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, 0.0, 0.0)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
if name == 'mobius':
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, 0.0, 0.0)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
if name == 'sphere':
# Gaussian curvature is 1/r^2
r = 10
gauss_curvature = 1.0 / r ** 2
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, gauss_curvature, gauss_curvature)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
p.point_data.SetActiveScalars(curvature)
scalar_range_curvatures = curvatures.update().output.GetPointData().GetScalars(curvature).range
bands = get_bands(scalar_range_curvatures, scalar_bar_labels)
freq = get_frequencies(bands, p)
bands, freq = adjust_ranges(bands, freq)
if frequency_table:
# Let's do a frequency table with the number of scalars in each band.
print_bands_frequencies(curvature, bands, freq)
lut = get_diverging_lut()
lut.table_range = scalar_range_curvatures
return {'surface': p, 'scalar_range_curvatures': scalar_range_curvatures, 'scalar_bar_labels': scalar_bar_labels,
'lut': lut}
def generate_mean_curvatures(surface, needs_adjusting, frequency_table=False):
"""
Generate the mean curvatures on the surface.
:param surface: The surface.
:param needs_adjusting: Surfaces whose curvatures need to be adjusted along the edges of the surface or constrained.
:param frequency_table: True if a frequency table is to be displayed.
:return: Return the surface, the scalar ranges of the curvatures along with the lookup tables.
"""
name = surface.name
source = surface.source
curvature = 'Mean_Curvature'
scalar_bar_labels = 5
curvatures = vtkCurvatures(curvature_type=Curvatures.CurvatureType.VTK_CURVATURE_MEAN)
p = (source >> curvatures).update().output
if name in needs_adjusting:
adjust_edge_curvatures(p, curvature)
if name == 'bour':
# Mean curvature is 0
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, 0, 0)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
if name == 'enneper':
# Mean curvature is 0
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, 0, 0)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
if name == 'cube':
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, 0.0, 0.0)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
if name == 'mobius':
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, -0.6, 0.6)
if name == 'sphere':
# Mean curvature is 1/r
r = 10
mean_curvature = 1.0 / r
constrain_curvatures(p, curvature, mean_curvature, mean_curvature)
scalar_bar_labels = 1
p.point_data.SetActiveScalars(curvature)
scalar_range_curvatures = curvatures.update().output.GetPointData().GetScalars(curvature).range
bands = get_bands(scalar_range_curvatures, scalar_bar_labels)
freq = get_frequencies(bands, p)
bands, freq = adjust_ranges(bands, freq)
if frequency_table:
# Let's do a frequency table with the number of scalars in each band.
print_bands_frequencies(curvature, bands, freq)
lut = get_diverging_lut1()
lut.table_range = scalar_range_curvatures
return {'surface': p, 'scalar_range_curvatures': scalar_range_curvatures, 'scalar_bar_labels': scalar_bar_labels,
'lut': lut}
def adjust_edge_curvatures(source, curvature_name, epsilon=1.0e-08):
"""
This function adjusts curvatures along the edges of the surface by replacing
the value with the average value of the curvatures of points in the neighborhood.
:param source: The vtkCurvatures object.
:param curvature_name: The name of the curvature, 'Gauss_Curvature' or 'Mean_Curvature'.
:param epsilon: Absolute curvature values less than this will be set to zero.
:return:
"""
def point_neighbourhood(pt_id):
"""
Extract the topological neighbors for point.
:param pt_id: The point id.
:return: The neighbour ids.
"""
cell_ids = vtkIdList()
source.GetPointCells(pt_id, cell_ids)
neighbour = set()
for cell_idx in range(0, cell_ids.GetNumberOfIds()):
cell_id = cell_ids.GetId(cell_idx)
cell_point_ids = vtkIdList()
source.GetCellPoints(cell_id, cell_point_ids)
for cell_pt_idx in range(0, cell_point_ids.GetNumberOfIds()):
neighbour.add(cell_point_ids.GetId(cell_pt_idx))
return neighbour
def compute_distance(pt_id_a, pt_id_b):
"""
Compute the distance between two points given their ids.
:param pt_id_a: First point.
:param pt_id_b: Second point.
:return: The distance.
"""
pt_a = np.array(source.GetPoint(pt_id_a))
pt_b = np.array(source.GetPoint(pt_id_b))
return np.linalg.norm(pt_a - pt_b)
# Get the active scalars
source.point_data.SetActiveScalars(curvature_name)
np_source = dsa.WrapDataObject(source)
curvatures = np_source.PointData[curvature_name]
# Get the boundary point IDs.
array_name = 'ids'
id_filter = vtkGenerateIds(point_ids=True, cell_ids=False,
point_ids_array_name=array_name,
cell_ids_array_name=array_name)
edges = vtkFeatureEdges(boundary_edges=True, manifold_edges=False,
non_manifold_edges=False, feature_edges=False)
(source >> id_filter >> edges).update()
edge_array = edges.output.GetPointData().GetArray(array_name)
boundary_ids = []
for i in range(edges.output.GetNumberOfPoints()):
boundary_ids.append(edge_array.GetValue(i))
# Remove duplicate Ids.
p_ids_set = set(boundary_ids)
# Iterate over the edge points and compute the curvature as the weighted
# average of the neighbours.
count_invalid = 0
for p_id in boundary_ids:
p_ids_neighbors = point_neighbourhood(p_id)
# Keep only interior points.
p_ids_neighbors -= p_ids_set
# Compute distances and extract curvature values.
curvs = [curvatures[p_id_n] for p_id_n in p_ids_neighbors]
dists = [compute_distance(p_id_n, p_id) for p_id_n in p_ids_neighbors]
curvs = np.array(curvs)
dists = np.array(dists)
curvs = curvs[dists > 0]
dists = dists[dists > 0]
if len(curvs) > 0:
weights = 1 / np.array(dists)
weights /= weights.sum()
new_curv = np.dot(curvs, weights)
else:
# Corner case.
count_invalid += 1
# Assuming the curvature of the point is planar.
new_curv = 0.0
# Set the new curvature value.
curvatures[p_id] = new_curv
# Set small values to zero.
if epsilon != 0.0:
curvatures = np.where(abs(curvatures) < epsilon, 0, curvatures)
curv = numpy_support.numpy_to_vtk(num_array=curvatures.ravel(),
deep=True,
array_type=VTK_DOUBLE)
curv.name = curvature_name
source.point_data.RemoveArray(curvature_name)
source.point_data.AddArray(curv)
source.point_data.active_scalars = curvature_name
def constrain_curvatures(source, curvature_name, lower_bound=0.0, upper_bound=0.0):
"""
This function constrains curvatures to the range [lower_bound ... upper_bound].
Remember to update the vtkCurvatures object before calling this.
:param source: A vtkPolyData object corresponding to the vtkCurvatures object.
:param curvature_name: The name of the curvature, 'Gauss_Curvature' or 'Mean_Curvature'.
:param lower_bound: The lower bound.
:param upper_bound: The upper bound.
:return:
"""
bounds = list()
if lower_bound < upper_bound:
bounds.append(lower_bound)
bounds.append(upper_bound)
else:
bounds.append(upper_bound)
bounds.append(lower_bound)
# Get the active scalars
source.point_data.SetActiveScalars(curvature_name)
np_source = dsa.WrapDataObject(source)
curvatures = np_source.PointData[curvature_name]
# Set upper and lower bounds.
curvatures = np.where(curvatures < bounds[0], bounds[0], curvatures)
curvatures = np.where(curvatures > bounds[1], bounds[1], curvatures)
curv = numpy_support.numpy_to_vtk(num_array=curvatures.ravel(),
deep=True,
array_type=VTK_DOUBLE)
curv.name = curvature_name
source.point_data.RemoveArray(curvature_name)
source.point_data.AddArray(curv)
source.point_data.active_scalars = curvature_name
def get_diverging_lut():
"""
See: [Diverging Color Maps for Scientific Visualization](https://www.kennethmoreland.com/color-maps/)
start point midPoint end point
cool to warm: 0.230, 0.299, 0.754 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.706, 0.016, 0.150
purple to orange: 0.436, 0.308, 0.631 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.759, 0.334, 0.046
green to purple: 0.085, 0.532, 0.201 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.436, 0.308, 0.631
blue to brown: 0.217, 0.525, 0.910 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.677, 0.492, 0.093
green to red: 0.085, 0.532, 0.201 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.758, 0.214, 0.233
:return:
"""
ctf = vtkColorTransferFunction(color_space=ColorTransferFunction.ColorSpace.VTK_CTF_DIVERGING)
# Cool to warm.
ctf.AddRGBPoint(0.0, 0.230, 0.299, 0.754)
ctf.AddRGBPoint(0.5, 0.865, 0.865, 0.865)
ctf.AddRGBPoint(1.0, 0.706, 0.016, 0.150)
table_size = 256
lut = vtkLookupTable(number_of_table_values=table_size)
lut.Build()
for i in range(0, table_size):
rgba = list(ctf.GetColor(float(i) / table_size)) + [1.0]
lut.SetTableValue(i, rgba)
return lut
def get_diverging_lut1():
colors = vtkNamedColors()
# Colour transfer function.
ctf = vtkColorTransferFunction(color_space=ColorTransferFunction.ColorSpace.VTK_CTF_DIVERGING)
p1 = [0.0] + list(colors.GetColor3d('MidnightBlue'))
p2 = [0.5] + list(colors.GetColor3d('Gainsboro'))
p3 = [1.0] + list(colors.GetColor3d('DarkOrange'))
ctf.AddRGBPoint(*p1)
ctf.AddRGBPoint(*p2)
ctf.AddRGBPoint(*p3)
table_size = 256
lut = vtkLookupTable(number_of_table_values=table_size)
lut.Build()
for i in range(0, table_size):
rgba = list(ctf.GetColor(float(i) / table_size)) + [1.0]
lut.SetTableValue(i, rgba)
return lut
def get_source(source, available_surfaces):
"""
:param source: The name of the source.
:param available_surfaces: The surfaces
:return:
"""
surface = source.lower()
if surface not in available_surfaces:
return None
elif surface == 'bour':
return get_bour()
elif surface == 'cube':
return get_cube()
elif surface == 'enneper':
return get_enneper()
elif surface == 'hills':
return get_hills()
elif surface == 'mobius':
return get_mobius()
elif surface == 'random hills':
return get_random_hills()
elif surface == 'sphere':
return get_sphere()
elif surface == 'torus':
return get_torus()
return None
def get_bour():
surface = vtkParametricBour()
u_resolution = 50
v_resolution = 50
source = vtkParametricFunctionSource(parametric_function=surface,
u_resolution=u_resolution, v_resolution=v_resolution,
generate_texture_coordinates=True)
# Build the tangents.
tangents = vtkPolyDataTangents()
transform = vtkTransform()
transform.RotateX(-90.0)
transform_filter = vtkTransformPolyDataFilter(transform=transform)
return source >> tangents >> transform_filter
def get_cube():
surface = vtkCubeSource()
# Triangulate.
triangulation = vtkTriangleFilter()
# Subdivide the triangles.
subdivide = vtkLinearSubdivisionFilter(number_of_subdivisions=3)
# Build the tangents.
tangents = vtkPolyDataTangents()
return surface >> triangulation >> subdivide >> tangents
def get_hills():
"""
Create four hills on a plane.
This will have regions of negative, zero and positive Gaussian curvatures.
:return:
"""
x_res = 50
y_res = 50
x_min = -5.0
x_max = 5.0
dx = (x_max - x_min) / (x_res - 1)
y_min = -5.0
y_max = 5.0
dy = (y_max - y_min) / (x_res - 1)
# Make a grid.
# We define the parameters for the hills here.
# There are four hills.
# [[0: x0, 1: y0, 2: x variance, 3: y variance, 4: amplitude]...]
hd = [[-2.5, -2.5, 2.5, 6.5, 3.5], [2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 2],
[5.0, -2.5, 1.5, 1.5, 2.5], [-5.0, 5, 2.5, 3.0, 3]]
# Three hills.
# hd = [[-2.5, -2.5, 2.5, 6.5, 3.5], [-5.0, 5, 2.5, 3.0, 3], [5.0, -2.5, 1.5, 1.5, 2.5]]
# Two hills.
# hd = [[5.0, -2.5, 1.5, 1.5, 2.5], [-5.0, 5, 2.5, 3.0, 3]]
xx = [0.0] * 2
# Generate the points.
y = y_min
xyz = list()
for r in range(x_res):
x = x_min
for c in range(y_res):
z = 0
for j in range(0, len(hd)):
xx[0] = (x - hd[j][0] / hd[j][2]) ** 2.0
xx[1] = (y - hd[j][1] / hd[j][3]) ** 2.0
z += hd[j][4] * math.exp(-(xx[0] + xx[1]) / 2.0)
xyz.append([x, y, z])
x += dx
y += dy
np_xyz = np.array(xyz)
points = vtkPoints(data=numpy_support.numpy_to_vtk(np_xyz))
# print(points)
# Triangulate each quad.
triangles = vtkCellArray()
t_num = 0
for r in range(0, x_res - 1):
for c in range(0, y_res - 1):
indices = list()
# We select the index of each point so that
# the ordering is counterclockwise.
rc = r * y_res
# Triangle 1.
indices.append(rc + c)
indices.append(indices[0] + 1)
indices.append(rc + y_res + c)
# print(f't_num: {t_num} :- {indices[0]}, {indices[1]}, {indices[2]}')
triangle = vtkTriangle()
for i in range(0, len(indices)):
triangle.GetPointIds().SetId(i, indices[i])
triangles.InsertNextCell(triangle)
indices.clear()
t_num += 1
# Triangle 2.
indices.append(rc + c + 1)
indices.append(rc + y_res + c + 1)
indices.append(rc + y_res + c)
# print(f't_num: {t_num} :- {indices[0]}, {indices[1]}, {indices[2]}')
triangle = vtkTriangle()
for i in range(0, len(indices)):
triangle.GetPointIds().SetId(i, indices[i])
triangles.InsertNextCell(triangle)
indices.clear()
t_num += 1
poly_data = vtkPolyData(points=points, polys=triangles)
textures = vtkFloatArray(name='Textures', number_of_components=2, number_of_tuples=2 * poly_data.number_of_points)
poly_data.GetPointData().SetTCoords(textures)
for i in range(0, x_res):
tc = [i / (x_res - 1.0), 0.0]
for j in range(0, y_res):
# tc[1] = 1.0 - j / (y_res - 1.0)
tc[1] = j / (y_res - 1.0)
textures.SetTuple(i * y_res + j, tc)
bounds = poly_data.bounds
elevation_filter = vtkElevationFilter(low_point=(0.0, 0.0, bounds[4]), high_point=(0.0, 0.0, bounds[5]))
normals = vtkPolyDataNormals(feature_angle=30, splitting=False)
transform = vtkTransform()
# transform.Translate(0.0, 5.0, 15.0)
transform.RotateX(-90.0)
transform_filter = vtkTransformPolyDataFilter(transform=transform)
return poly_data >> elevation_filter >> normals >> transform_filter
def get_enneper():
surface = vtkParametricEnneper()
u_resolution = 50
v_resolution = 50
source = vtkParametricFunctionSource(parametric_function=surface,
u_resolution=u_resolution, v_resolution=v_resolution,
generate_texture_coordinates=True)
# Build the tangents.
tangents = vtkPolyDataTangents()
transform = vtkTransform()
transform.RotateX(-90.0)
transform_filter = vtkTransformPolyDataFilter(transform=transform)
return source >> tangents >> transform_filter
def get_mobius():
minimum_v = -0.25
maximum_v = 0.25
surface = vtkParametricMobius(minimum_v=minimum_v, maximum_v=maximum_v, )
u_resolution = 50
v_resolution = 50
source = vtkParametricFunctionSource(parametric_function=surface,
u_resolution=u_resolution, v_resolution=v_resolution,
generate_texture_coordinates=True)
# Build the tangents.
tangents = vtkPolyDataTangents()
transform = vtkTransform()
transform.RotateX(-90.0)
transform_filter = vtkTransformPolyDataFilter(transform=transform)
return source >> tangents >> transform_filter
def get_random_hills():
random_seed = 1
number_of_hills = 30
# If you want a plane
# hill_amplitude=0
surface = vtkParametricRandomHills(random_seed=random_seed, number_of_hills=number_of_hills)
u_resolution = 50
v_resolution = 50
source = vtkParametricFunctionSource(parametric_function=surface,
u_resolution=u_resolution, v_resolution=v_resolution,
generate_texture_coordinates=True)
# Build the tangents.
tangents = vtkPolyDataTangents()
transform = vtkTransform()
transform.Translate(0.0, 5.0, 15.0)
transform.RotateX(-90.0)
transform_filter = vtkTransformPolyDataFilter(transform=transform)
return source >> tangents >> transform_filter
def get_sphere():
theta_resolution = 32
phi_resolution = 32
surface = vtkTexturedSphereSource(theta_resolution=theta_resolution, phi_resolution=phi_resolution)
# Now the tangents.
tangents = vtkPolyDataTangents()
return surface >> tangents
def get_torus():
surface = vtkParametricTorus()
u_resolution = 50
v_resolution = 50
source = vtkParametricFunctionSource(parametric_function=surface,
u_resolution=u_resolution, v_resolution=v_resolution,
generate_texture_coordinates=True)
# Build the tangents.
tangents = vtkPolyDataTangents()
transform = vtkTransform()
transform.RotateX(-90.0)
transform_filter = vtkTransformPolyDataFilter(transform=transform)
return source >> tangents >> transform_filter
def get_frequencies(bands, src):
"""
Count the number of scalars in each band.
The scalars used are the active scalars in the polydata.
:param: bands - The bands.
:param: src - The vtkPolyData source.
:return: The frequencies of the scalars in each band.
"""
freq = dict()
for i in range(len(bands)):
freq[i] = 0
tuples = src.point_data.GetScalars().GetNumberOfTuples()
for i in range(tuples):
x = src.point_data.GetScalars().GetTuple1(i)
for j in range(len(bands)):
if x <= bands[j][2]:
freq[j] += 1
break
return freq
def adjust_ranges(bands, freq):
"""
The bands and frequencies are adjusted so that the first and last
frequencies in the range are non-zero.
:param bands: The bands dictionary.
:param freq: The frequency dictionary.
:return: Adjusted bands and frequencies.
"""
# Get the indices of the first and last non-zero elements.
first = 0
for k, v in freq.items():
if v != 0:
first = k
break
rev_keys = list(freq.keys())[::-1]
last = rev_keys[0]
for idx in list(freq.keys())[::-1]:
if freq[idx] != 0:
last = idx
break
# Now adjust the ranges.
min_key = min(freq.keys())
max_key = max(freq.keys())
for idx in range(min_key, first):
freq.pop(idx)
bands.pop(idx)
for idx in range(last + 1, max_key + 1):
freq.popitem()
bands.popitem()
old_keys = freq.keys()
adj_freq = dict()
adj_bands = dict()
for idx, k in enumerate(old_keys):
adj_freq[idx] = freq[k]
adj_bands[idx] = bands[k]
return adj_bands, adj_freq
def get_bands(d_r, number_of_bands, precision=2, nearest_integer=False):
"""
Divide a range into bands
:param: d_r - [min, max] the range that is to be covered by the bands.
:param: number_of_bands - The number of bands, a positive integer.
:param: precision - The decimal precision of the bounds.
:param: nearest_integer - If True then [floor(min), ceil(max)] is used.
:return: A dictionary consisting of the band number and [min, midpoint, max] for each band.
"""
prec = abs(precision)
if prec > 14:
prec = 14
bands = dict()
if (d_r[1] < d_r[0]) or (number_of_bands <= 0):
return bands
x = list(d_r)
if nearest_integer:
x[0] = math.floor(x[0])
x[1] = math.ceil(x[1])
dx = (x[1] - x[0]) / float(number_of_bands)
b = [x[0], x[0] + dx / 2.0, x[0] + dx]
i = 0
while i < number_of_bands:
b = list(map(lambda ele_b: round(ele_b, prec), b))
if i == 0:
b[0] = x[0]
bands[i] = b
b = [b[0] + dx, b[1] + dx, b[2] + dx]
i += 1
return bands
def print_bands_frequencies(curvature, bands, freq, precision=2):
prec = abs(precision)
if prec > 14:
prec = 14
if len(bands) != len(freq):
print('Bands and Frequencies must be the same size.')
return
s = f'Bands & Frequencies:\n{" ".join(curvature.lower().replace("_", " ").split()).title()}\n'
total = 0
width = prec + 6
for k, v in bands.items():
total += freq[k]
for j, q in enumerate(v):
if j == 0:
s += f'{k:4d} ['
if j == len(v) - 1:
s += f'{q:{width}.{prec}f}]: {freq[k]:8d}\n'
else:
s += f'{q:{width}.{prec}f}, '
width = 3 * width + 13
s += f'{"Total":{width}s}{total:8d}\n'
print(s)
class ScalarBarProperties:
"""
The properties needed for scalar bars.
"""
named_colors = vtkNamedColors()
lut = None
# These are in pixels
maximum_dimensions = {'width': 100, 'height': 260}
title_text = '',
number_of_labels: int = 5
label_format = '{:0.2f}'
# Orientation vertical=True, horizontal=False.
orientation: bool = True
# Horizontal and vertical positioning.
# These are the default positions, don't change these.
default_v = {'p': (0.85, 0.05), 'p2': (0.1, 0.7)}
default_h = {'p': (0.125, 0.05), 'p2': (0.75, 0.1)}
# Modify these as needed.
position_v = copy.deepcopy(default_v)
position_h = copy.deepcopy(default_h)
def make_scalar_bar_widget(scalar_bar_properties, title_text_property, label_text_property, renderer,
interactor):
"""
Make a scalar bar widget.
:param scalar_bar_properties: The lookup table, title name, maximum dimensions in pixels and position.
:param title_text_property: The properties for the title.
:param label_text_property: The properties for the labels.
:param renderer: The default renderer.
:param interactor: The vtkInteractor.
:return: The scalar bar widget.
"""
sb_actor = vtkScalarBarActor(lookup_table=scalar_bar_properties.lut, title=scalar_bar_properties.title_text,
unconstrained_font_size=True,
number_of_labels=scalar_bar_properties.number_of_labels,
title_text_property=title_text_property, label_text_property=label_text_property,
label_format=scalar_bar_properties.label_format,
)
sb_rep = vtkScalarBarRepresentation(enforce_normalized_viewport_bounds=True,
orientation=scalar_bar_properties.orientation)
# Set the position.
sb_rep.position_coordinate.SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport()
sb_rep.position2_coordinate.SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport()
if scalar_bar_properties.orientation:
sb_rep.position_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_v['p']
sb_rep.position2_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_v['p2']
else:
sb_rep.position_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_h['p']
sb_rep.position2_coordinate.value = scalar_bar_properties.position_h['p2']
widget = vtkScalarBarWidget(representation=sb_rep, scalar_bar_actor=sb_actor, default_renderer=renderer,
interactor=interactor, enabled=True)
return widget
def get_text_positions(names, justification=0, vertical_justification=0, width=0.96, height=0.1):
"""
Get viewport positioning information for a list of names.
:param names: The list of names.
:param justification: Horizontal justification of the text, default is left.
:param vertical_justification: Vertical justification of the text, default is bottom.
:param width: Width of the bounding_box of the text in screen coordinates.
:param height: Height of the bounding_box of the text in screen coordinates.
:return: A list of positioning information.
"""
# The gap between the left or right edge of the screen and the text.
dx = 0.02
width = abs(width)
if width > 0.96:
width = 0.96
y0 = 0.01
height = abs(height)
if height > 0.9:
height = 0.9
dy = height
if vertical_justification == TextProperty.VerticalJustification.VTK_TEXT_TOP:
y0 = 1.0 - (dy + y0)
dy = height
if vertical_justification == TextProperty.VerticalJustification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED:
y0 = 0.5 - (dy / 2.0 + y0)
dy = height
name_len_min = 0
name_len_max = 0
first = True
for k in names:
sz = len(k)
if first:
name_len_min = name_len_max = sz
first = False
else:
name_len_min = min(name_len_min, sz)
name_len_max = max(name_len_max, sz)
text_positions = dict()
for k in names:
sz = len(k)
delta_sz = width * sz / name_len_max
if delta_sz > width:
delta_sz = width
if justification == TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_CENTERED:
x0 = 0.5 - delta_sz / 2.0
elif justification == TextProperty.Justification.VTK_TEXT_RIGHT:
x0 = 1.0 - dx - delta_sz
else:
# Default is left justification.
x0 = dx
# For debugging!
# print(
# f'{k:16s}: (x0, y0) = ({x0:3.2f}, {y0:3.2f}), (x1, y1) = ({x0 + delta_sz:3.2f}, {y0 + dy:3.2f})'
# f', width={delta_sz:3.2f}, height={dy:3.2f}')
text_positions[k] = {'p': [x0, y0, 0], 'p2': [delta_sz, dy, 0]}
return text_positions
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ColorTransferFunction:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ColorSpace:
VTK_CTF_RGB: int = 0
VTK_CTF_HSV: int = 1
VTK_CTF_LAB: int = 2
VTK_CTF_DIVERGING: int = 3
VTK_CTF_LAB_CIEDE2000: int = 4
VTK_CTF_STEP: int = 5
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Scale:
VTK_CTF_LINEAR: int = 0
VTK_CTF_LOG10: int = 1
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Curvatures:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class CurvatureType:
VTK_CURVATURE_GAUSS: int = 0
VTK_CURVATURE_MEAN: int = 1
VTK_CURVATURE_MAXIMUM: int = 2
VTK_CURVATURE_MINIMUM: int = 3
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Mapper:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ColorMode:
VTK_COLOR_MODE_DEFAULT: int = 0
VTK_COLOR_MODE_MAP_SCALARS: int = 1
VTK_COLOR_MODE_DIRECT_SCALARS: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ResolveCoincidentTopology:
VTK_RESOLVE_OFF: int = 0
VTK_RESOLVE_POLYGON_OFFSET: int = 1
VTK_RESOLVE_SHIFT_ZBUFFER: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class ScalarMode:
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_DEFAULT: int = 0
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_POINT_DATA: int = 1
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_CELL_DATA: int = 2
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_POINT_FIELD_DATA: int = 3
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_CELL_FIELD_DATA: int = 4
VTK_SCALAR_MODE_USE_FIELD_DATA: int = 5
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Curvatures:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class CurvatureType:
VTK_CURVATURE_GAUSS: int = 0
VTK_CURVATURE_MEAN: int = 1
VTK_CURVATURE_MAXIMUM: int = 2
VTK_CURVATURE_MINIMUM: int = 3
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class TextProperty:
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Justification:
VTK_TEXT_LEFT: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_RIGHT: int = 2
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class VerticalJustification:
VTK_TEXT_BOTTOM: int = 0
VTK_TEXT_CENTERED: int = 1
VTK_TEXT_TOP: int = 2
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
main(sys.argv)