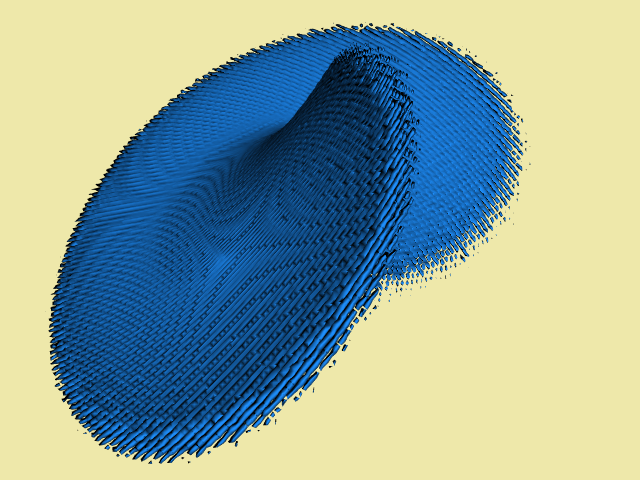
Lorenz
Repository source: Lorenz
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
Lorenz.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Create an iso-surface of the Lorenz attractor.
Here we visualize a Lorenz strange attractor by integrating the Lorenz equations in a volume.
The number of visits in each voxel is recorded as a scalar function.
The surface is extracted via a contour filter using a visit value of 50.
The number of integration steps is 10 million, in a volume of dimensions 200 x 200 x 200.
The surface roughness is caused by the discrete nature of the evaluation function.
"""
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkInteractionStyle
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkRenderingOpenGL2
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonColor import vtkNamedColors
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonCore import (
vtkMinimalStandardRandomSequence,
vtkShortArray
)
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonDataModel import vtkStructuredPoints
from vtkmodules.vtkFiltersCore import vtkContourFilter
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingCore import (
vtkActor,
vtkPolyDataMapper,
vtkRenderWindow,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor,
vtkRenderer
)
def main():
colors = vtkNamedColors()
Pr = 10.0 # The Lorenz parameters
b = 2.667
r = 28.0
# x = 0.0
# y = 0.0
# z = 0.0 # starting (and current) x, y, z
h = 0.01 # integration step size
resolution = 200 # slice resolution
iterations = 10000000 # number of iterations
xmin = -30.0 # x, y, z range for voxels
xmax = 30.0
ymin = -30.0
ymax = 30.0
zmin = -10.0
zmax = 60.0
# Take a stab at an integration step size.
dx = resolution / (xmax - xmin)
dy = resolution / (ymax - ymin)
dz = resolution / (zmax - zmin)
s = 'The Lorenz Attractor\n'
s += f' Pr = {Pr}\n b = {b}\n r = {r}\n'
s += f' integration step size = {h:4.2f}\n'
s += f' slice resolution = {resolution}\n'
s += f' number of iterations = {iterations}\n'
s += f' specified range (x, y, z):\n'
s += f' minimum: ({xmin:6.2f}, {ymin:6.2f}, {zmin:6.2f})\n'
s += f' maximum: ({xmax:6.2f}, {ymax:6.2f}, {zmax:6.2f})\n'
print(s)
random_sequence = vtkMinimalStandardRandomSequence(seed=8775070)
x = random_sequence.GetRangeValue(xmin, xmax)
random_sequence.Next()
y = random_sequence.GetRangeValue(ymin, ymax)
random_sequence.Next()
z = random_sequence.GetRangeValue(zmin, zmax)
random_sequence.Next()
s += f' starting at: ({x:6.2f}, {y:6.2f}, {z:6.2f})'
print(s)
print(' generating the volume ...')
# Allocate memory for the slices.
slice_size = resolution * resolution
num_pts = slice_size * resolution
scalars = vtkShortArray()
for i in range(0, num_pts):
scalars.InsertTuple1(i, 0)
for j in range(0, iterations):
# Integrate to the next time step.
xx = x + h * Pr * (y - x)
yy = y + h * (x * (r - z) - y)
zz = z + h * (x * y - (b * z))
x = xx
y = yy
z = zz
# Calculate the voxel index.
if xmax > x > xmin and ymax > y > ymin and zmax > z > zmin:
xxx = int(float(xx - xmin) * dx)
yyy = int(float(yy - ymin) * dy)
zzz = int(float(zz - zmin) * dz)
index = xxx + yyy * resolution + zzz * slice_size
scalars.SetTuple1(index, scalars.GetTuple1(index) + 1)
origin = (xmin, ymin, zmin)
spacing = ((xmax - xmin) / resolution, (ymax - ymin) / resolution, (zmax - zmin) / resolution)
volume = vtkStructuredPoints(dimensions=(resolution, resolution, resolution),
origin=origin, spacing=spacing)
volume.point_data.SetScalars(scalars)
print(' contouring ...')
# Create the iso-surface.
contour = vtkContourFilter(input_data=volume)
contour.SetValue(0, 50)
# Create mapper.
mapper = vtkPolyDataMapper(scalar_visibility=False)
contour >> mapper
# Create actor.
actor = vtkActor(mapper=mapper)
actor.property.color = colors.GetColor3d('DodgerBlue')
# Do the graphics dance.
renderer = vtkRenderer(background=colors.GetColor3d('PaleGoldenrod'))
ren_win = vtkRenderWindow(size=(640, 480), window_name='Lorenz')
ren_win.AddRenderer(renderer)
iren = vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
iren.render_window = ren_win
renderer.AddActor(actor)
# Interact with the data.
ren_win.Render()
ren_win.SetWindowName('Lorenz')
camera = renderer.active_camera
camera.position = (-67.645167, -25.714343, 63.483516)
camera.focal_point = (3.224902, -4.398594, 29.552112)
camera.view_up = (-0.232264, 0.965078, 0.121151)
camera.distance = 81.414176
camera.clipping_range = (18.428905, 160.896031)
iren.Start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()